There are some new techniques for reducing the risk of HIV transmission when attempting to get pregnant.
If you are a woman living with HIV who has either a single or a same-sex relationship. Due to advances in treatment in HIV care, many HIV-positive women live longer, healthier lives. As HIV-positive women think about their future, some are planning to have the babies they’ve always wanted.
Many women in the world have HIV and many of these women are suffering from childlessness.
The Great news is that advancements in HIV care have also dramatically decreased the risk of a mother passing HIV on to her baby (often known as perinatal HIV transmission, or vertical transmission, also referred to as mother-to-child transmission). The World Health Organization estimates that HIV can be spread prenatally as much as 45% of the time when women are not taking HIV medications.
After all, with HIV treatment, the risk of perinatal transmission could be less than five in 100 births.
Also according to The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC), if a woman takes HIV drugs and is virally suppressed (the amounts of virus in her blood, identified as her viral load, is impossible to detect with regular tests), the chances of transmission could be less than one in 100. It is also important to note that studies have shown that pregnancy will not increase the progress of HIV in the mother.
Before getting pregnant
If applicable, it is essential to plan carefully before you get pregnant:
Share your plans with your HIV healthcare professional to ensure that you are on the correct treatment plan for your health and to reduce the risk of perinatal transmission (more on this in the next sections). If you are currently taking an HIV drug containing dolutegravir (Tivicay, also present in Juluca and Triumeq), address the potential risk of birth defects with your HIV health care provider.
Find an obstetrician (OB) or midwife who is familiar with HIV treatment. Your choices for getting pregnant with as little danger as possible should be clarified to your partner. For more information on getting pregnant and strategies for a healthy pregnancy, see our Getting Pregnant and HIV fact sheet.
Tell your HIV health care provider and your OB or midwife to speak to each other and coordinate their treatment before and during pregnancy.
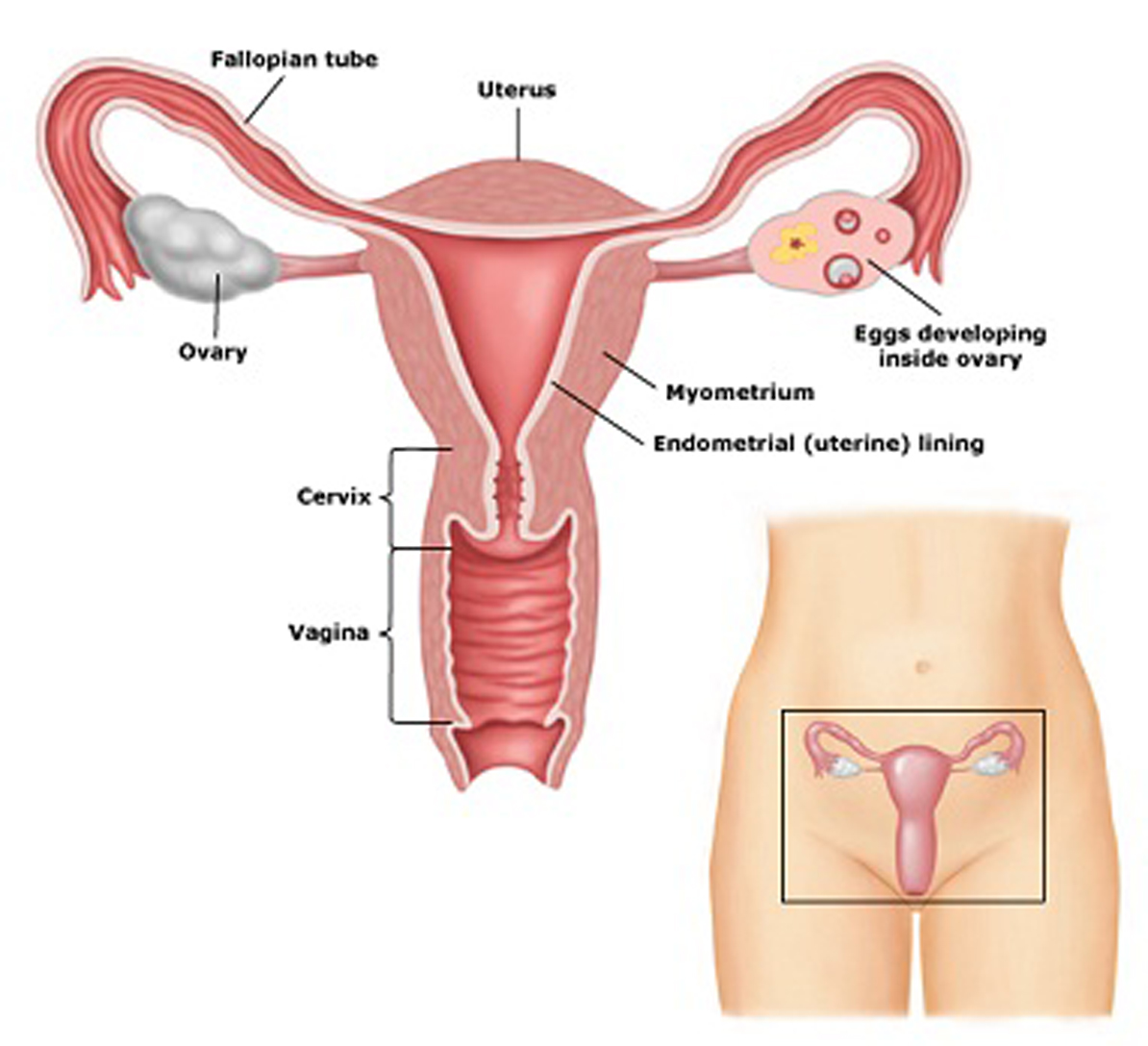
Get tested for sexually transmitted infections or diseases (STIs or STDs), hepatitis B and C, and tuberculosis.
Keep taking pregnancy vitamins (‘prenatal’ vitamins) that contain folic acid when you are pregnant. This can minimize the rates of certain birth defects.
If friends and family do not support your decision to have a child, set up a support network of people who are compassionate, non-judgmental, and well informed about HIV and pregnancy. Your network can include health care professionals, counsellors, and other HIV-positive women who are pregnant or have had children.
Guidelines for pregnancy
Several groups of pregnancy experts in HIV-positive women have established recommendations that guide proper care and treatment for HIV-positive women who are or may become pregnant.
As a first step, the pregnancy recommendations released by the US Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) suggest a comprehensive check-up, including a range of blood tests, to find out about your health and the status of your HIV infection. A resistance test (see our resistance fact sheet for information on this test) should be used if you.
Here are some alternative options below that will help you to understand what might be best for you and prepare you to discuss with your health care provider.
Sperm from Donor
Donor sperm comes from a sperm bank or from someone you know about. Sperm donors to sperm banks are most frequently anonymous and have been checked for fertility and disease to ensure the Sperm mix is healthy and able to induce pregnancy.
Before trying intrauterine insemination (IUI), people trying to conceive might be pulled to at-home conception HIV. Take The V-conceive home insemination kit from shubhag.in, an insemination syringe kit designed for women for insemination at home and designed to help couples with unexplained infertility, the LGBTQ community, women with the vagina, endometriosis, and tilted uterus, malefactors (low motility, sperm count, and performance anxiety) as well as single mothers by preference.
Home insemination: A guide for women living with HIV
This includes the use of donor sperm from someone you know or from a sperm bank. Not every state allows sperm from a sperm bank that can be used for insemination at home. If you can use a sperm donor from a sperm bank for home insemination in your state, ask your sperm bank for guidance on how to use the sperm at home.
If you’re using semen from someone you know, have a man ejaculate (cum) in a clean container or condom. If you are using a condom, make sure to use one without spermicide. Then, using a syringe (without a needle), you suck the semen and inject the syringe deep inside the vagina. When the syringe is deep inside the vagina, the syringe is closed and the semen is collected.
How to make home insemination successful
Based on the individual experience and at least one analysis, it is often suggested that after using home insemination with a syringe a woman lies down for 20 minutes after injecting semen to boost fertility. You can have non-needle syringes at most in every pharmacy since they are widely used to give medicines to infants. Your HIV provider may have some to offer you as well.
You can get this home insemination kit online India by shubhag.in.
Assisted Reproduction
This means that an egg is fertilized by a sperm with the help of a medical technique or therapy. Assisted reproduction (sometimes called “assisted reproductive technology”) is helpful when the future parent(s) require help to prevent HIV transmission between partners, are using donor sperm, or are having trouble getting pregnant at home because of fertility issues. Unfortunately, few facilities offer assisted reproduction to people living with HIV, and few health insurance schemes cover it.
Artificial Insemination Treat
The process can be used for many types of fertility problems. In cases involving male infertility, it is often used when there is a very low sperm count or when sperm is not strong enough to swim through the cervix and the fallopian tubes.
Here V-conceive home insemination kit helps plan your future or get pregnant.
Home IUI treatment for Unexplained Infertility couples
If you are facing unexplained infertility V-conceive home insemination kit by Shubhag.in helps for unexplained infertility in couples.
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART includes taking a combination of HIV drugs (called HIV care regimens) every day.
ART is recommended for all people who have HIV. ART cannot cure HIV, but HIV medicines help people with HIV to live longer, healthier lives. ART Bills also reduces the risk of transmission of HIV.
How are HIV medicines working?
HIV targets and kills the immune system’s CD4-fighting cells. Loss of CD4 cells makes it impossible for the body to control diseases and some HIV-related cancers.
HIV medicines prevent the multiplying of HIV (copy of themselves) which reduces the amount of HIV in the body (called the viral load). Having fewer HIV in the body gives the immune system a chance to regenerate and create more CD4 cells. While there is still some HIV in the body, the immune system is strong enough to combat infections and even HIV-related cancers.
HIV drugs also greatly reduce the risk of HIV transmission by reducing the amount of HIV in the body. The main aim of HIV care is to reduce the viral load of a person to an undetectable amount. An undetectable viral load means that the amount of HIV in the blood is too low for a viral load test to be identified.
People with HIV who maintain an undetectable viral load effectively have no danger of HIV transmission by sex to their HIV-negative partners.
Using Home insemination Benefits
Home insemination can be a beneficial and successful treatment for some couples who have difficulty in conceiving. Some of the conditions the doctor may recommend for artificial insemination include:
- Couples where a man may have a genetic defect and donor sperm is desired
- Men with a low sperm count
- Men with low motility of sperm
- Women whose cervical mucus can be unfavourable to pregnancy
- Women with a history of endometriosis
Artificial insemination also provides the prospect that a single woman or a same-sex couple could become pregnant through donated sperm.
Success rates for home insemination
The same study found a 40.5 percent success rate for IUI after 6 treatments.
Along with an article in the Journal of Andrology, IUI pregnancy success rates are higher after six IUI cycles compared to the same number of ICI cycles. This is possibly due to the more direct positioning and storage of highly concentrated sperm. According to the University of Wisconsin Hospitals and Clinics, storing a sperm sample in a laboratory raises the concentration of sperm by 20 times.





